0% found this document useful (0 votes)
160 views7 pagesOverview of Art Historical Periods
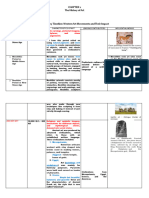
The document provides an overview of major art periods from the Stone Age through the 19th century, listing the characteristic styles, notable artists, and concurrent historical events for each period. It covers prehistoric cave paintings, Mesopotamian relief sculptures, Egyptian tomb art, Greek idealism and architecture, Roman realism and engineering, Byzantine mosaics and Islamic architecture, Renaissance revivals of classical styles, Baroque religious art, Neoclassical emulation of antiquity, Romantic exaltation of imagination, and Realist celebrations of everyday life. Key developments and figures are noted for each era to connect the visual arts with broader historical contexts.
Uploaded by
aasis21Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
160 views7 pagesOverview of Art Historical Periods
The document provides an overview of major art periods from the Stone Age through the 19th century, listing the characteristic styles, notable artists, and concurrent historical events for each period. It covers prehistoric cave paintings, Mesopotamian relief sculptures, Egyptian tomb art, Greek idealism and architecture, Roman realism and engineering, Byzantine mosaics and Islamic architecture, Renaissance revivals of classical styles, Baroque religious art, Neoclassical emulation of antiquity, Romantic exaltation of imagination, and Realist celebrations of everyday life. Key developments and figures are noted for each era to connect the visual arts with broader historical contexts.
Uploaded by
aasis21Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd