0% found this document useful (0 votes)
149 views12 pagesBalanced Scorecard: Performance Management Guide
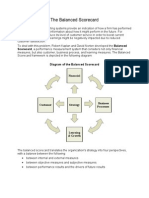
The Balanced Scorecard is a performance management tool used by management teams to evaluate organizational performance across four key perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. It was developed in the 1990s as an extension of traditional financial metrics to include additional dimensions of performance. The Balanced Scorecard translates an organization's vision and strategy into objectives and measures across the four perspectives, and allows organizations to track strategic performance and link long-term strategic objectives to short-term actions.
Uploaded by
api-457966545Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
149 views12 pagesBalanced Scorecard: Performance Management Guide
The Balanced Scorecard is a performance management tool used by management teams to evaluate organizational performance across four key perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. It was developed in the 1990s as an extension of traditional financial metrics to include additional dimensions of performance. The Balanced Scorecard translates an organization's vision and strategy into objectives and measures across the four perspectives, and allows organizations to track strategic performance and link long-term strategic objectives to short-term actions.
Uploaded by
api-457966545Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd