0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views1 pageJava Program for Counting Integers
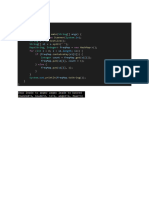
This document contains code for a program that counts the frequency of integers in an input. It uses an ArrayList to store the integers and a HashMap to count frequencies. The program iterates through the input n times, adding each integer to the ArrayList and HashMap. It then iterates through the ArrayList again to print each integer and its frequency before setting the frequency to null. The overall time complexity of the algorithm is O(n).
Uploaded by
MilenaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views1 pageJava Program for Counting Integers
This document contains code for a program that counts the frequency of integers in an input. It uses an ArrayList to store the integers and a HashMap to count frequencies. The program iterates through the input n times, adding each integer to the ArrayList and HashMap. It then iterates through the ArrayList again to print each integer and its frequency before setting the frequency to null. The overall time complexity of the algorithm is O(n).
Uploaded by
MilenaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd