100% found this document useful (1 vote)
738 views27 pagesIntroduction To Wesm PDF
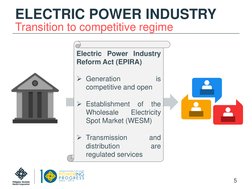
1) The document introduces the Wholesale Electricity Spot Market (WESM) in the Philippines, which was established through the Electric Power Industry Reform Act to introduce competition in power generation.
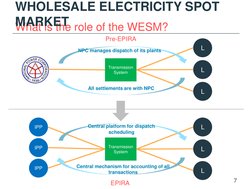
2) The WESM serves as a central platform for scheduling, pricing, and settling electricity transactions between generation companies, distribution utilities, and directly connected customers.
3) The key processes in the WESM include registration of participants, scheduling of generation based on offers and bids, determination of locational marginal pricing, dispatch of schedules, and settlement of transactions.
Uploaded by
ambonulanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
738 views27 pagesIntroduction To Wesm PDF
1) The document introduces the Wholesale Electricity Spot Market (WESM) in the Philippines, which was established through the Electric Power Industry Reform Act to introduce competition in power generation.
2) The WESM serves as a central platform for scheduling, pricing, and settling electricity transactions between generation companies, distribution utilities, and directly connected customers.
3) The key processes in the WESM include registration of participants, scheduling of generation based on offers and bids, determination of locational marginal pricing, dispatch of schedules, and settlement of transactions.
Uploaded by
ambonulanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to WESM: Overview of the Wholesale Electricity Spot Market (WESM) and its purpose in the power industry.
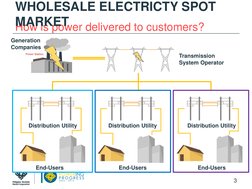
- What is the WESM?: Defines the concept of the WESM and its role in delivering electricity to customers.
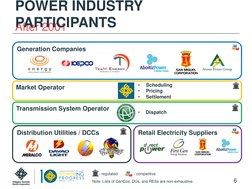
- Industry Participants: Discusses the various participants in the power industry before and after the establishment of competitive regimes.
- Transition to Competitive Regime: Explains the transition to a competitive electricity market under the Electric Power Industry Reform Act.
- Role and Advantages of WESM: Details the operational role of WESM and the advantages it offers in power market transparency and efficiency.
- Market Processes: Describes the specific processes involved in WESM operations, including registration, scheduling, pricing, dispatch, and settlement.
- Typical Day for Participants: Illustrates typical daily activities and interactions for generation companies and customers within WESM.
- WESM Governance: Overview of the governance structure, committees, and regulations overseeing WESM operations.
- Mitigating Measures: Outlines measures designed to manage price caps and ensure market stability.
- WESM Mindanao: Provides information on the launch and operational setup of WESM in the Mindanao region.
- End of Presentation: Concludes the presentation with contact information and final statements about WESM.