0% found this document useful (0 votes)
301 views4 pagesOrthopedic Assessment Guide
The document outlines the typical steps in an orthopedic physiotherapy assessment:
1. Obtaining patient history including chief complaint, medical history, and pain details.
2. Observation of the affected area without touching, noting things like swelling, gait, and deformities.
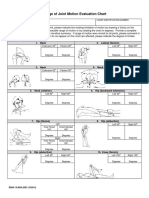
3. Examination of the affected area with touching, including range of motion tests, muscle strength tests, and reflex tests.
4. Palpation of the affected area to check for movements and contours.
5. Performing special tests designed for diagnostic confirmation.
6. Assessing joint movement, reflexes, and cutaneous sensation.
7. Obtaining diagnostic imaging reports like X-rays to confirm conditions.
Uploaded by
arushiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
301 views4 pagesOrthopedic Assessment Guide
The document outlines the typical steps in an orthopedic physiotherapy assessment:
1. Obtaining patient history including chief complaint, medical history, and pain details.
2. Observation of the affected area without touching, noting things like swelling, gait, and deformities.
3. Examination of the affected area with touching, including range of motion tests, muscle strength tests, and reflex tests.
4. Palpation of the affected area to check for movements and contours.
5. Performing special tests designed for diagnostic confirmation.
6. Assessing joint movement, reflexes, and cutaneous sensation.
7. Obtaining diagnostic imaging reports like X-rays to confirm conditions.
Uploaded by
arushiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd