0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 views8 pagesIntroduction to RDBMS Concepts
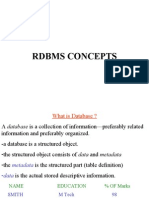
Concurrent Access - Allowing multiple users to access a database at the same time. Data administration - Managing the structure and content of a database. Database - An organized collection of related data stored together in one or more files or tables.
Database system - Software that allows users to define, create, maintain and control access to the database. DBA - Database Administrator who is responsible for the design, implementation, and maintenance of the database. Integration - Combining related information from different sources into a unified database. Integrity - Ensuring data is valid, accurate and consistent.
Persistent data - Data that remains stored in a database even after the
Uploaded by
Umer RashidCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 views8 pagesIntroduction to RDBMS Concepts
Concurrent Access - Allowing multiple users to access a database at the same time. Data administration - Managing the structure and content of a database. Database - An organized collection of related data stored together in one or more files or tables.
Database system - Software that allows users to define, create, maintain and control access to the database. DBA - Database Administrator who is responsible for the design, implementation, and maintenance of the database. Integration - Combining related information from different sources into a unified database. Integrity - Ensuring data is valid, accurate and consistent.
Persistent data - Data that remains stored in a database even after the
Uploaded by
Umer RashidCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd