0% found this document useful (0 votes)
268 views12 pagesJSP Guide for Developers
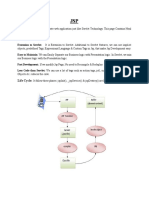
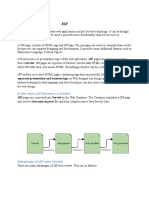
JSP (Java Server Pages) allows developers to create dynamic web pages by mixing static HTML markup with special JSP tags that generate dynamic content. JSP pages are compiled into Java servlets that generate output for the browser. This makes developing dynamic web applications with JSP easier than manually writing Java servlets. JSP supports common elements like scriptlets, expressions, directives, and declarations to add dynamic functionality to web pages. JSP pages follow a lifecycle of translation, compilation, loading, request handling, and destruction similar to servlets.
Uploaded by
minniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
268 views12 pagesJSP Guide for Developers
JSP (Java Server Pages) allows developers to create dynamic web pages by mixing static HTML markup with special JSP tags that generate dynamic content. JSP pages are compiled into Java servlets that generate output for the browser. This makes developing dynamic web applications with JSP easier than manually writing Java servlets. JSP supports common elements like scriptlets, expressions, directives, and declarations to add dynamic functionality to web pages. JSP pages follow a lifecycle of translation, compilation, loading, request handling, and destruction similar to servlets.
Uploaded by
minniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 12