0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views6 pagesPemrograman dan Struktur Data 2019
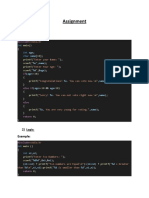
The document is a summary of tasks for the Programming and Data Structures course. It includes the lecturer's name, the student's name and student ID, and their program of study at the University of Education Ganesha in 2019.
Uploaded by
winda damayantiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views6 pagesPemrograman dan Struktur Data 2019
The document is a summary of tasks for the Programming and Data Structures course. It includes the lecturer's name, the student's name and student ID, and their program of study at the University of Education Ganesha in 2019.
Uploaded by
winda damayantiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd