0% found this document useful (0 votes)
115 views9 pagesPanel Data Analysis of Dependent Variable Y
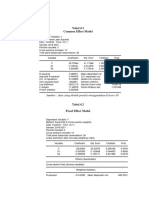
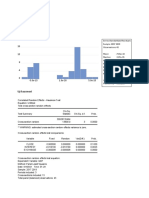
The summary provides descriptive statistics for variables Y, X1 through X5 from a dataset. For each variable it reports the mean, median, maximum, minimum, standard deviation, skewness, kurtosis, Jarque-Bera statistic, probability, sum, sum of squared deviations, number of observations. The Jarque-Bera statistic tests for normality and the lower the probability value, the more the series deviates from normal.
Uploaded by
Yohanes SephaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
115 views9 pagesPanel Data Analysis of Dependent Variable Y
The summary provides descriptive statistics for variables Y, X1 through X5 from a dataset. For each variable it reports the mean, median, maximum, minimum, standard deviation, skewness, kurtosis, Jarque-Bera statistic, probability, sum, sum of squared deviations, number of observations. The Jarque-Bera statistic tests for normality and the lower the probability value, the more the series deviates from normal.
Uploaded by
Yohanes SephaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd