50% found this document useful (2 votes)
227 views64 pagesHitler's Path to Power in Germany
Hitler rose to power in Germany after World War 1. He gained support by blaming the country's problems on Jews and others. His Nazi party used violent tactics to eliminate opposition. After being imprisoned for treason, Hitler reorganized the party and won elections, becoming Chancellor in 1933. He then consolidated power and established a single party fascist state, enacting racist laws targeting Jews. This set Germany on a path to war and the Holocaust.
Uploaded by
Nicole LongCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
50% found this document useful (2 votes)
227 views64 pagesHitler's Path to Power in Germany
Hitler rose to power in Germany after World War 1. He gained support by blaming the country's problems on Jews and others. His Nazi party used violent tactics to eliminate opposition. After being imprisoned for treason, Hitler reorganized the party and won elections, becoming Chancellor in 1933. He then consolidated power and established a single party fascist state, enacting racist laws targeting Jews. This set Germany on a path to war and the Holocaust.
Uploaded by
Nicole LongCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to Hitler’s Rise: This section introduces Adolf Hitler and the main focus of the presentation on his rise to power in Nazi Germany.
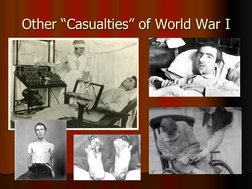
- World War I and Its Aftermath: Discusses the impacts of World War I, focusing on destruction and death toll, setting the stage for the rise of discontent.
- Treaty of Versailles and Weimar Government: Covers the Treaty of Versailles obligations and the instability of the Weimar Republic.
- Adolf Hitler’s Early Life and Rise: Explores Hitler’s early life, rise to prominence, and how he influenced Germany post-WWI.
- Formation of the Nazi Party: Details the formation of the Nazi Party and Hitler’s role within it, including key events like the Beer Hall Putsch.
- Hitler’s Policies and Pre-War Actions: Examines Hitler’s strategic policies and actions leading up to World War II, focusing on military expansion and propaganda campaigns.
- Anti-Semitic Policies and Actions: Discusses the anti-Semitic measures taken by Hitler and the Nazi regime, including the Nuremberg Laws and Kristallnacht.
- Conclusion and Future Outlook: Concludes with a reflection on what the future held for Hitler and the Nazi regime, indicating ongoing conflict and tensions.