0% found this document useful (0 votes)
928 views5 pagesSecurity Profiles - Inspection Modes
This document provides information about configuring various security profiles on FortiGate devices, including inspection modes (flow-based vs proxy-based), antivirus, web filtering, DNS filtering, application control, intrusion prevention, file filtering, email filtering, data leak prevention, VoIP, ICAP, web application firewalling, and SSL/SSH inspection. It describes the differences between flow-based and proxy-based inspection, listing which features each security profile supports in each mode.
Uploaded by
Ayan NasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
928 views5 pagesSecurity Profiles - Inspection Modes
This document provides information about configuring various security profiles on FortiGate devices, including inspection modes (flow-based vs proxy-based), antivirus, web filtering, DNS filtering, application control, intrusion prevention, file filtering, email filtering, data leak prevention, VoIP, ICAP, web application firewalling, and SSL/SSH inspection. It describes the differences between flow-based and proxy-based inspection, listing which features each security profile supports in each mode.
Uploaded by
Ayan NasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Security Profiles: Provides an overview of configuring FortiGate security features including advanced inspection and protection capabilities.
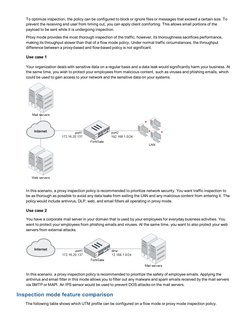
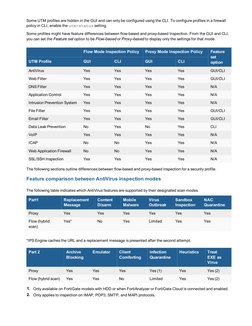
- Inspection Modes: Describes different inspection modes for firewall policies, detailing flow-based and proxy-based inspection techniques.
- Use Cases: Illustrates practical use cases demonstrating how different inspection modes can be applied to enhance security.
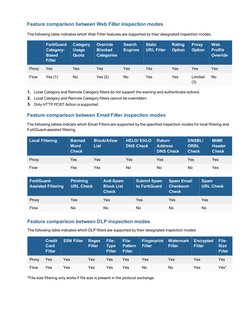
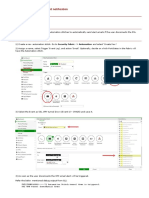
- Feature Comparison: Compares features supported by flow and proxy mode inspections across various modules like antivirus and application control.