0% found this document useful (0 votes)
203 views30 pagesUnderstanding Java Inheritance Concepts
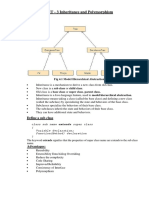
The document discusses inheritance in Java. It defines inheritance as a mechanism that allows a class to inherit properties from another class. The key points are:
- Inheritance allows code reuse, enhancement, adaptation and method overriding for runtime polymorphism.
- There are different types of inheritance including single, multiple, hierarchical, multilevel and hybrid inheritance.
- Access modifiers like public, protected and private determine which methods can be accessed in subclasses.
- The super keyword is used to access properties and methods of the parent class from the subclass.
- Constructors can call parent or sibling constructors using super() or this() respectively for constructor chaining.
Uploaded by
ijoollee biyyaaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
203 views30 pagesUnderstanding Java Inheritance Concepts
The document discusses inheritance in Java. It defines inheritance as a mechanism that allows a class to inherit properties from another class. The key points are:
- Inheritance allows code reuse, enhancement, adaptation and method overriding for runtime polymorphism.
- There are different types of inheritance including single, multiple, hierarchical, multilevel and hybrid inheritance.
- Access modifiers like public, protected and private determine which methods can be accessed in subclasses.
- The super keyword is used to access properties and methods of the parent class from the subclass.
- Constructors can call parent or sibling constructors using super() or this() respectively for constructor chaining.
Uploaded by
ijoollee biyyaaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd