0% found this document useful (0 votes)
443 views6 pagesSolid State - Point Defect
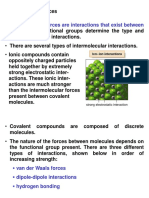
There are three main types of point defects in solids:
1. Stoichiometric defects include vacancies where atoms are missing from lattice sites, and interstitials where atoms occupy spaces between lattice sites.
2. Non-stoichiometric defects involve excess or deficiencies of atoms, such as metal deficiency or excess defects.
3. Impurity defects occur when foreign atoms are introduced into the solid structure.
Specific examples of stoichiometric defects mentioned are vacancy defects, interstitial defects, Frenkel defects, and Schottky defects.
Uploaded by
Siddharth palCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
443 views6 pagesSolid State - Point Defect
There are three main types of point defects in solids:
1. Stoichiometric defects include vacancies where atoms are missing from lattice sites, and interstitials where atoms occupy spaces between lattice sites.
2. Non-stoichiometric defects involve excess or deficiencies of atoms, such as metal deficiency or excess defects.
3. Impurity defects occur when foreign atoms are introduced into the solid structure.
Specific examples of stoichiometric defects mentioned are vacancy defects, interstitial defects, Frenkel defects, and Schottky defects.
Uploaded by
Siddharth palCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd