0% found this document useful (0 votes)
69 views2 pagesFormative Assessment Tools Guide
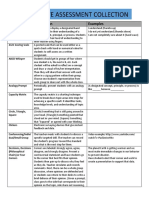
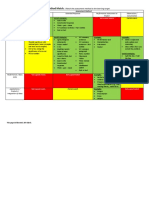
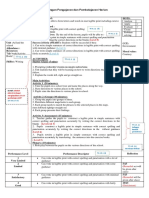
The document outlines various tools and techniques for formative assessment to check for student understanding. Methods include index cards, hand signals, one-minute essays, and concept maps, among others. Each technique is designed to encourage student reflection and engagement with the material being taught.
Uploaded by
priyaa guptaaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
69 views2 pagesFormative Assessment Tools Guide
The document outlines various tools and techniques for formative assessment to check for student understanding. Methods include index cards, hand signals, one-minute essays, and concept maps, among others. Each technique is designed to encourage student reflection and engagement with the material being taught.
Uploaded by
priyaa guptaaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd