100% found this document useful (1 vote)
997 views2 pagesVsepr Handout
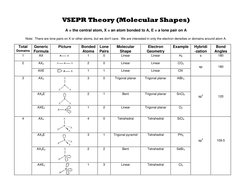
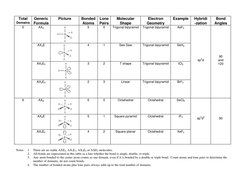
VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Theory predicts molecular geometry and structure based on the number of electron domains around a central atom. It states that electron domains will adopt an arrangement that minimizes repulsions between domains. The key factors considered are the central atom, number of bonded atoms, and lone pairs. Depending on the total number of domains, the molecular shape could be linear, bent, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, or octahedral.
Uploaded by
20718 LAY BUFFON FERNANDO GROSSOCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
997 views2 pagesVsepr Handout
VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Theory predicts molecular geometry and structure based on the number of electron domains around a central atom. It states that electron domains will adopt an arrangement that minimizes repulsions between domains. The key factors considered are the central atom, number of bonded atoms, and lone pairs. Depending on the total number of domains, the molecular shape could be linear, bent, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, or octahedral.
Uploaded by
20718 LAY BUFFON FERNANDO GROSSOCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- VSEPR Theory