0% found this document useful (0 votes)
69 views2 pagesStandard Proctor
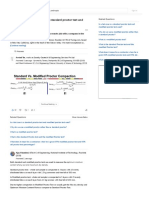
The Standard Proctor test determines the maximum dry density and optimum moisture content of soil, conforming to ASTM D698, and is used to assess the relative compaction of fill soils. The modified Proctor test (ASTM D1557) provides similar results but typically yields a higher maximum dry density. Typical values for various soil types are provided, along with additional soil properties that may be relevant.
Uploaded by
MuluCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
69 views2 pagesStandard Proctor
The Standard Proctor test determines the maximum dry density and optimum moisture content of soil, conforming to ASTM D698, and is used to assess the relative compaction of fill soils. The modified Proctor test (ASTM D1557) provides similar results but typically yields a higher maximum dry density. Typical values for various soil types are provided, along with additional soil properties that may be relevant.
Uploaded by
MuluCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd