0% found this document useful (0 votes)
413 views16 pagesLesson 1 - Levers and Pivots: Physics - Key Stage 3 Forces at Work
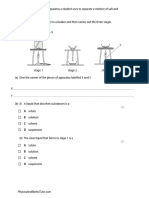
The document discusses levers and pivots, explaining that a lever is a simple machine that is a rigid object that can rotate around a fixed point called a pivot. It provides examples of levers like doors, wheelbarrows, and spanners. The key concept covered is that increasing either the force applied or the perpendicular distance between the force and the pivot can increase the turning effect or moment of the force.
Uploaded by
Niyi OmodaraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
413 views16 pagesLesson 1 - Levers and Pivots: Physics - Key Stage 3 Forces at Work
The document discusses levers and pivots, explaining that a lever is a simple machine that is a rigid object that can rotate around a fixed point called a pivot. It provides examples of levers like doors, wheelbarrows, and spanners. The key concept covered is that increasing either the force applied or the perpendicular distance between the force and the pivot can increase the turning effect or moment of the force.
Uploaded by
Niyi OmodaraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd