0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7K views9 pagesMySql Queries
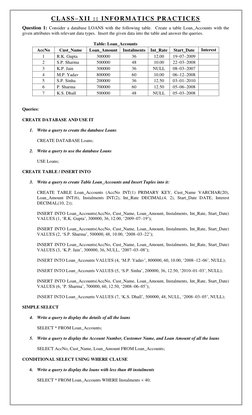
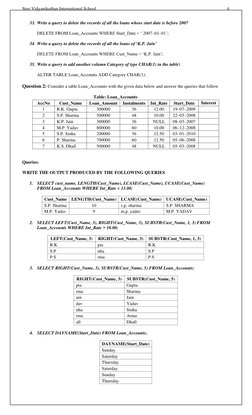
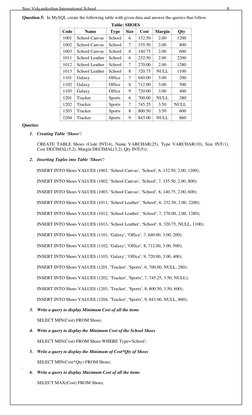
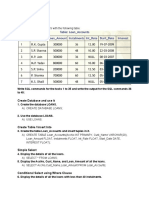
The document contains a database schema for a Loans database with a Loan_Accounts table. It provides 35 SQL queries to:
1) Create the Loans database and Loan_Accounts table
2) Insert records into the Loan_Accounts table
3) Perform simple, conditional, logical, and aggregate queries on the table like selecting, updating, deleting records
4) Use various SQL clauses like WHERE, ORDER BY, GROUP BY, JOIN etc.
Uploaded by
Svis TptyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7K views9 pagesMySql Queries
The document contains a database schema for a Loans database with a Loan_Accounts table. It provides 35 SQL queries to:
1) Create the Loans database and Loan_Accounts table
2) Insert records into the Loan_Accounts table
3) Perform simple, conditional, logical, and aggregate queries on the table like selecting, updating, deleting records
4) Use various SQL clauses like WHERE, ORDER BY, GROUP BY, JOIN etc.
Uploaded by
Svis TptyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd