0% found this document useful (0 votes)
197 views1 pageTheory of Structures: Module 2 Overview
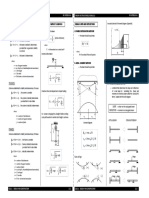
This document discusses several methods for analyzing structures and calculating deflections, including:
1. Three-moment equation and moment distribution method for indeterminate beams.
2. Virtual work equation and Castigliano's theorem for deflection of trusses and frames using virtual work principles.
3. Fixed-end moment calculation using integration for any loading condition on a beam with fixed supports.
It also provides an approximate analysis method for cantilever structures by assuming points of inflection and proportional axial forces.
Uploaded by
Maevin WooCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
197 views1 pageTheory of Structures: Module 2 Overview
This document discusses several methods for analyzing structures and calculating deflections, including:
1. Three-moment equation and moment distribution method for indeterminate beams.
2. Virtual work equation and Castigliano's theorem for deflection of trusses and frames using virtual work principles.
3. Fixed-end moment calculation using integration for any loading condition on a beam with fixed supports.
It also provides an approximate analysis method for cantilever structures by assuming points of inflection and proportional axial forces.
Uploaded by
Maevin WooCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd