0% found this document useful (0 votes)
151 views27 pagesEarly Heart Development in Embryos
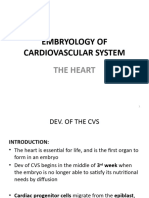
1. Early heart development begins with the formation of two primordial heart tubes from cardiogenic mesoderm around day 18 of development.
2. The heart tubes fuse to form a single median heart tube, which undergoes looping known as dextrocardia or a D-loop to position the developing chambers and vessels in their correct anatomical locations.
3. Partitioning of the heart tube into four chambers and great vessels is accomplished through the growth of endocardial cushions and septa within the tubular heart.
Uploaded by
Alena JosephCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
151 views27 pagesEarly Heart Development in Embryos
1. Early heart development begins with the formation of two primordial heart tubes from cardiogenic mesoderm around day 18 of development.
2. The heart tubes fuse to form a single median heart tube, which undergoes looping known as dextrocardia or a D-loop to position the developing chambers and vessels in their correct anatomical locations.
3. Partitioning of the heart tube into four chambers and great vessels is accomplished through the growth of endocardial cushions and septa within the tubular heart.
Uploaded by
Alena JosephCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd