0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes) 77 views13 pagesUntitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content,
claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
NAME: CLASS:
1. Two balloons, X and Y, are suspended by insulating threads. They are each held near a
negatively charged balloon. The balloons hang as shown.
/_— insulating. insulating ~
threads threads.
‘What is the charge on balloon X and what is the charge on balloon Y?
balloon X | _ balloon Y
negative negative
negative positive
positive negative
positive positive
[pom
2 Two metal spheres P and Q are mounted on insulating stands and are touching each other.
They are uncharged. A positively-charged metal sphere on an insulating handle is brought
close to P but does not touch it. This induces charges on P and Q.
positively-charged
‘metal sphere
The positively-charged metal sphere is held in this position and sphere Q is moved to the
right, away from sphere P. What are the signs of the induced charges on P and Q and how do
the sizes of these charges compare?
charge onP | charge onQ sizes of the
charges
A| negative positive equal
B| negative positive unequal
C| positive negative equal
D positive negative unequal�3
To charge an isolated metal sphere by induction, the following four processes are required
P- The sphere is earthed by touching it
Q- The earth connection is removed from the sphere.
R- Accharged rod is brought close to the sphere.
S- The charged rod is removed.
In which order can these stages be carried out to charge the isolated metal sphere?
A P+Q—-R+S B P-R+S—Q
© R+P>Q+8 D R>P+S+Q
A charge of 45 C flows through an electric appliance in 3.0 minutes. What is the average
current in the appliance?
A 0.258 B 40A Cc 15A D 135A
‘An ammeter is used to measure the current in a 300 © resistor. The ammeter is shown below.
—fO
are
Oo mA
What is the current reading across the resistor?
A 4.0mA B 4.2mA Cc 44mA D 4.6mA
The diagram shows a simple electric circuit.
+
‘Which row describes the charge on an electron and the direction of electron flow through the
resistor?
charge on | direction of
anelectron | electron flow
A| negative -to+
B | negative +t0-
© | positive -to+
D | positive +t0-�4
7 Which object will have the greatest change in electrical energy?
A Anelectron moved through a potential of 2.0 V.
B Anelectron moved through a potential of 4.0 V.
© Ametal sphere with a charge of 1.0 x 10°C moved through a potential difference of 2.0 V.
D_Ametal sphere with a charge of 1.0 x 10°C moved through a potential difference of 4.0 V.
8 A potential difference of 10 volts exists between two points, A and B, within an electric field.
‘What is the magnitude of charge that requires 2.0 x 10° kilojoule of work to move it from A to
B?
A 5.0% 10°C B 20x10'C © 50x 107C D 20x 10°C
9 If 60 joules of work is required to move 5.0 coulombs of charge between two points in an
electric field, what is the potential difference between these points?
A 0.005 KV B 0.012kV © 0.060 kV D 0.300 kV
10. The table below lists various characteristics of two metallic wires, A and B.
Gross-
Wire Material | TEMPErature | | onath(m) | sectional | Resistance
ee Area (m*) (a)
A Silver 20 0.10 0.010 R
8 Silver 20 0.20 0.020 2
If wire A has resistance R, then wire B has resistance
AR B2R © R2 D4R
44 Which changes would cause the greatest increase in the rate of flow of charge through a
conducting wire?
A increasing the applied potential difference and decreasing the length of wire
B increasing the applied potential difference and increasing the length of wire
© decreasing the applied potential difference and decreasing the length of wire
D decreasing the applied potential difference and increasing the length of wire
12. Several pieces of copper wire, all having the same length but different diameters, are kept at
room temperature. Which graph best represents the resistance, R, of the wires as a function
of their cross-sectional areas, A?
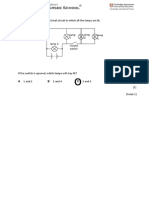
NEUBK�13. The diagram shows a circuit.
Which circuit diagram represents this?
Jao
414. Resistors of 1.0.9, 2.0, and 3.0 9 are connected in parallel with a cell. Which statement is.
correct?
A The current in each resistor is different but the potential difference (p.d.) across each
resistor is the same.
B The current in each resistor is the same but the potential difference across each resistor is
different.
© The potential difference across the 3.0 0. is greater than the potential difference across the
1.0.0 resistor.
D The sum of the potential differences across each resistor is equal to the electromotive
force (e.m-f.) of the cell�6
15. Two resistors of 6 Q and 12 0 are arranged in parallel. A p.d. is connected across the
terminals X and Y. The current through the 6 © resistor is 4 A.
62 an
What is the current in the ammeter?
A4A B 6A c BA D 124
16 Which costs the most if operated from the same mains supply?
‘A 25000 W electric cooker used for 1 minute
B a 1000 Welectric fire used for 10 minutes
© 2500 Welectric iron used for 1 hour
“D2 100 W lamp used for 1 day
17 An immersion heater is labelled 12 V, 60 W. What is the current in the heater when connected
toa 12 V supply?
A 020A 'B50A c 12A D 60A
18 Power can be represented in variety of ways except for
A Vxl BFR c
v
OR
19 An engineer uses the potential divider shown in the diagram. He needs the output voltage to
be one tenth (1) of the input voltage.
| x
output
| Y | voltage
input
voltage
Which pair of values could he use for the two resistors X and Y?
x/kO YIkQ
A 1.0 9.0
B 1.0 10.0
c 9.0 1.0
D 10.0 1.0�7
20 When the thermistor in the circuit below is heated, the current in the lamp increases.
Why does this happen?
‘A. The resistance of the lamp decreases.
B_ The resistance of the lamp increases.
© The resistance of the thermistor decreases.
D The resistance of the thermistor increases.
21. The diagram shows a circuit with a fixed resistor connected in series with a light-dependent
resistor (LOR). A voltmeter is connected across the LDR.
A bright lamp shines light onto the LDR. The lamp is then switched off and this causes the
voltmeter reading to change. Which row shows the change in the resistance of the LDR and
the change in the voltmeter reading when the lamp is switched off?
resistance of | voltmeter
LOR reading
A | decreases | decreases
B | decreases increases
C | increases decreases
D increases increases�It Aye
We «A
=
:
ee
How can the nail be demagnetised?
@))
removing the nail from the coil while using an a.c. supply
leaving the apparatus switched on for a long time
using a coil with fewer tums
using more cells
vom>
24 A magnet is placed close to an iron bar. The iron bar becomes an induced magnet.
“a
Which magnetic poles are formed at the ends X and Y of the bar?
end Y end X
A N N
B N s
c s N
D s s�9
25 The diagram below represents the magnetic field near point P.
Jy
If a compass is placed at point P in the same plane as the magnetic field, which arrow
represents the direction the north end of the compass needle will point?
if
26 Which of the lists of metals below contains only metals which are non-ferrous?
c D
A. iron, steel, nickel B cobalt, copper, steel
© aluminium, brass, copper D iron, tin, aluminium
27 Awite is placed between the poles of a horseshoe magnet. There is a current in the wire in
the direction shown, and this causes a force to act on the wire.
magnet
force
Three other arrangements, P, Q and R, of the wire and magnet are set up as shown.
Pp Q R
magnet tuned around current direction reversed —_current direction reversed
‘and magnet tumed around
Which arrangement or arrangements will cause a force in the same direction as the original
arrangement?
A P,QandR B PandQonly © Ponly D Ronly�10
28 The diagram shows a simple d.c. motor.
What is the part labelled Q?
A acoil B acommutator © amagnet D asiip ring
29° Two straight electrical conductors are parallel to one another. Each carries a current, one into
the plane of the paper and one out of the plane of the paper. Which diagram shows the
magnetic field around the two wires?
A B
‘current into
> ® plane of paper
© MuTent out of
plane of paper�"
30. Four metal rods are placed, in tum, inside a coil of copper wire.
‘current in coil
metal rod
Paper clips
Each rod is used to pick up as many paper clips as possible. The current is then switched off.
The table gives the results of the experiment. Which rod is the most suitable core for a coil in
a circuit breaker?
number of paper clips
picked up when there is
a current in the coil
A 1
B 20
c 35
D 35,
number of paper clips
still attached after the
current is switched off
0
2
0
30
31 The diagram shows a shaded area where the direction of a magnetic field is into the page. A
beam of electrons enters the field as shown.
beam of >
magnetic feld
into the page
x x x x xX)
x x x x x x
x x x x x x
x xX xX x x x
In which direction is the beam of electrons deflected as they enter the magnetic field?
A into the page B_outof the page © downthe page D_up the page�12
32. The diagram shows a transformer.
input output
voltage © voltage
primary coil secondary coil
800 turns 40 tums
The input voltage is 240 V. What is the output voltage?
A 60V B12V c 20V D 40v
33. The diagram shows an a.c. generator.
coil Gy
‘output voltage
As the coil passes through the position shown, the output voltage is +10 V. When does the
output voltage become -10 V?
‘A when the coil has tumed through 90° B_ when the coil has tumed through 180°
(© when the coil has tumed through 270° D_ when the coil has tumed through 360°�13
34 A transformer is needed to convert a supply of 240 V a.c. into 4800 V a.c.
Np Ng
240Va.c. 4800Va.c.
Which pair of coils would be suitable for this transformer?
number of tums on number of tums on
primary coil Np secondary coil Ns
a 50 1000
B 240 48000
c 480 24
D 2000 100
35 A magnet is suspended from a spring so that it can move freely inside a coil. The coil is
connected to a sensitive centre-zero ammeter.
Z
spring
‘moving magnet
N
centre-zeroammeter
stationary coil
What does the ammeter show when the magnet repeatedly moves slowly up and down?
Aa reading constantly changing from left to right and right to left
B a steady reading to the left
© asteady reading to the right
D_asteady reading of zero
36 A transformer is used to raise the voltage of electricity which is produced at a power station
for transmission in power lines. The power station produces 100 MW of power. The
transformer steps this up to a voltage of 400 KV for transmission in power lines. Assume that
the transformer is 100% efficient. What current flows in the power lines?
A 250A B 025A © 4x10A D 40,000A�14
37. Which of the following truth tables represents the behavior of a NAND gate?
A B
A B Y
0 o 1
0 1 0
1 0 0
1 1 0
alalool>
alolaoln
+|ololol|<)
38 The diagram shows a combination of logic gates.
input P
(9) ‘output X
input Q ‘output Y
e1)
Input P is at a logic state 0 (low) and input Q is at a logic state 1 (high). What are the logic
states at output X and at output Y?
‘output X ‘output ¥
A 0 0
B 0 1
c 1 0
D 1 1
39 How do you make a NAND gate out of an AND gate using inverters (NOT gate)?
A. Invert the output from the AND gate
B_ Invert both the inputs to the AND gate
© Invert one of the inputs to the AND gate
D Invert both the inputs and output of the AND gate
40. A simple lighting circuit contains two switches. If EITHER switch is pressed a lamp will light.
What type of logic gate is represented by the two switches?
A AND BOR © NAND D NOR