0% found this document useful (0 votes)
698 views20 pagesCVS - Charts & Diagrams
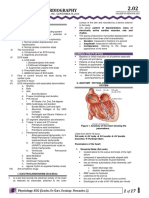
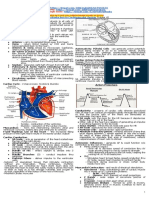
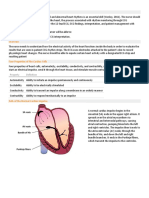
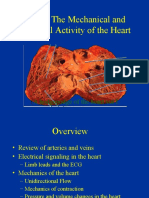
The document provides instructions for students to create diagrams and flowcharts related to the cardiovascular system and submit them by a deadline of May 15, 2023. It lists 19 topics for the diagrams and flowcharts to cover, including normal pressures within cardiac chambers, the action potential in different cardiac muscles, the conducting system of the heart, factors affecting cardiac output, regulation of blood pressure, and applied aspects of the cardiovascular response to different conditions like exercise and posture.
Uploaded by
MamathaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
698 views20 pagesCVS - Charts & Diagrams
The document provides instructions for students to create diagrams and flowcharts related to the cardiovascular system and submit them by a deadline of May 15, 2023. It lists 19 topics for the diagrams and flowcharts to cover, including normal pressures within cardiac chambers, the action potential in different cardiac muscles, the conducting system of the heart, factors affecting cardiac output, regulation of blood pressure, and applied aspects of the cardiovascular response to different conditions like exercise and posture.
Uploaded by
MamathaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd