0% found this document useful (0 votes)
102 views12 pagesAnalyzing Grid Structures with DSM
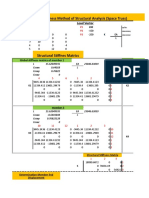
The document discusses using the direct stiffness method to analyze grid structures. Grid structures are structural systems defined by a network of intersecting members arranged in a regular pattern. The direct stiffness method involves breaking down a complex structure into smaller elements and calculating the stiffness of each element. These stiffness values are then assembled into a larger stiffness matrix that describes the overall behavior of the structure. The document outlines formulating the stiffness matrix for a grid structure by deriving element stiffness matrices in local coordinates and transforming them to global coordinates using a transformation matrix.
Uploaded by
Taha ShalabiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
102 views12 pagesAnalyzing Grid Structures with DSM
The document discusses using the direct stiffness method to analyze grid structures. Grid structures are structural systems defined by a network of intersecting members arranged in a regular pattern. The direct stiffness method involves breaking down a complex structure into smaller elements and calculating the stiffness of each element. These stiffness values are then assembled into a larger stiffness matrix that describes the overall behavior of the structure. The document outlines formulating the stiffness matrix for a grid structure by deriving element stiffness matrices in local coordinates and transforming them to global coordinates using a transformation matrix.
Uploaded by
Taha ShalabiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 12