0% found this document useful (0 votes)
55 views11 pagesEffective Kitchen Layouts for Restaurants
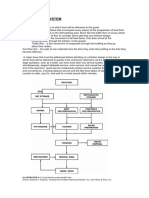
The document discusses kitchen layouts and design. It describes the importance of considering factors like energy efficiency, equipment placement, and ergonomics when designing a kitchen layout. The kitchen work triangle, which forms a rotational movement between cooking, chopping, and storage areas, is also discussed. Different types of kitchen configurations - including ergonomic, assembly line, zone, and island configurations - are outlined. Specific kitchen sections like the hot kitchen, cold kitchen, pastry kitchen, and larder kitchen are also described. Finally, the document provides examples of layouts for different food service outlets like hotels, restaurants, cafes, and fast food.
Uploaded by
mala hamdanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
55 views11 pagesEffective Kitchen Layouts for Restaurants
The document discusses kitchen layouts and design. It describes the importance of considering factors like energy efficiency, equipment placement, and ergonomics when designing a kitchen layout. The kitchen work triangle, which forms a rotational movement between cooking, chopping, and storage areas, is also discussed. Different types of kitchen configurations - including ergonomic, assembly line, zone, and island configurations - are outlined. Specific kitchen sections like the hot kitchen, cold kitchen, pastry kitchen, and larder kitchen are also described. Finally, the document provides examples of layouts for different food service outlets like hotels, restaurants, cafes, and fast food.
Uploaded by
mala hamdanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd