0% found this document useful (0 votes)
593 views14 pagesDomain, Range and Asymptotes: Chapter 2 / Example 7
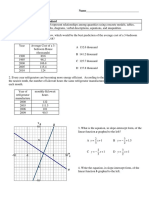
The document provides examples of using a Casio graphing calculator (GDC) to determine the domain, range, and asymptotes of rational functions by graphing and using a table of values. It also gives examples of using the GDC to solve absolute value equations and inequalities graphically. The examples demonstrate entering functions as Y-variables, adjusting the viewing window, finding intersections using G-Solve, and determining solutions from the intersections of the graphs.
Uploaded by
Diandra Satria AdhitamaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
593 views14 pagesDomain, Range and Asymptotes: Chapter 2 / Example 7
The document provides examples of using a Casio graphing calculator (GDC) to determine the domain, range, and asymptotes of rational functions by graphing and using a table of values. It also gives examples of using the GDC to solve absolute value equations and inequalities graphically. The examples demonstrate entering functions as Y-variables, adjusting the viewing window, finding intersections using G-Solve, and determining solutions from the intersections of the graphs.
Uploaded by
Diandra Satria AdhitamaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd