0% found this document useful (0 votes)
248 views3 pagesImprove COP in Vapor Compression Cycle
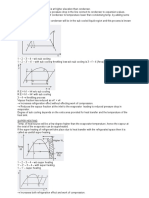
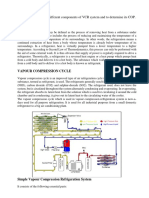
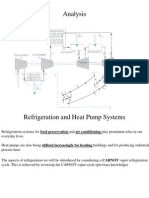
The document discusses four methods to improve the coefficient of performance (COP) in a vapor compression cycle: 1) Adding a flash chamber to separate unwanted vapor from liquid refrigerant before the evaporator, 2) Adding an accumulator to separate phases between the expansion device and evaporator, 3) Subcooling liquid refrigerant using vapor refrigerant in a heat exchanger, and 4) Subcooling liquid refrigerant using liquid refrigerant in a heat exchanger. These methods improve COP by reducing the amount of inactive vapor in the evaporator, allowing only liquid refrigerant to absorb heat, or increasing the enthalpy difference between evaporator and condenser states. Diagrams are provided to illustrate each method.
Uploaded by
Mainak PaulCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
248 views3 pagesImprove COP in Vapor Compression Cycle
The document discusses four methods to improve the coefficient of performance (COP) in a vapor compression cycle: 1) Adding a flash chamber to separate unwanted vapor from liquid refrigerant before the evaporator, 2) Adding an accumulator to separate phases between the expansion device and evaporator, 3) Subcooling liquid refrigerant using vapor refrigerant in a heat exchanger, and 4) Subcooling liquid refrigerant using liquid refrigerant in a heat exchanger. These methods improve COP by reducing the amount of inactive vapor in the evaporator, allowing only liquid refrigerant to absorb heat, or increasing the enthalpy difference between evaporator and condenser states. Diagrams are provided to illustrate each method.
Uploaded by
Mainak PaulCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd