0% found this document useful (0 votes)
798 views1 pageStarch Extraction
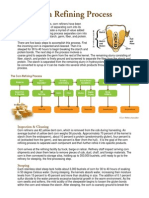
Starch can be extracted from grains or roots and tubers through two processes. For grains, the wet-milling process cleans, steeps, grinds the grain to remove non-starch components, then mixes the flour with water to remove gluten and yield crude starch milk, which is dewatered in hydrocyclones. For roots and tubers, cleaning and rasping breaks cell walls to release starch granules, followed by washing to flush granules from cells, with hydrocyclones then separating starch from water and fiber.
Uploaded by
Jolina ManuelCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
798 views1 pageStarch Extraction
Starch can be extracted from grains or roots and tubers through two processes. For grains, the wet-milling process cleans, steeps, grinds the grain to remove non-starch components, then mixes the flour with water to remove gluten and yield crude starch milk, which is dewatered in hydrocyclones. For roots and tubers, cleaning and rasping breaks cell walls to release starch granules, followed by washing to flush granules from cells, with hydrocyclones then separating starch from water and fiber.
Uploaded by
Jolina ManuelCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd