0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views1 pageHow a Bill Becomes Law: Step-by-Step Guide
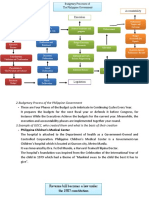
A bill becomes a law through an 11-step process involving drafting, introduction, committee review, floor debate, votes in the House and Senate, reconciliation if needed, and final presidential action. The bill is drafted, introduced in Congress, reviewed by committees, debated on the floors of each chamber, voted on, sent for reconciliation or to the president, who can sign it, veto it, or do nothing and allow it to become law.
Uploaded by
jsmnksm06Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views1 pageHow a Bill Becomes Law: Step-by-Step Guide
A bill becomes a law through an 11-step process involving drafting, introduction, committee review, floor debate, votes in the House and Senate, reconciliation if needed, and final presidential action. The bill is drafted, introduced in Congress, reviewed by committees, debated on the floors of each chamber, voted on, sent for reconciliation or to the president, who can sign it, veto it, or do nothing and allow it to become law.
Uploaded by
jsmnksm06Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd