0% found this document useful (0 votes)
579 views40 pagesClass 9 - Cell - Structural and Functional Unit of Life
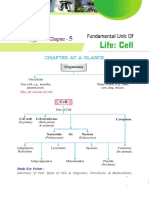
Cell- Structural and Functional unit of Life
[1] Cells are the fundamental unit of life and exist as either unicellular or multicellular organisms. [2] They were first observed under microscopes in the 17th century. [3] Cells vary in shape, size, and whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic.
Uploaded by
anyastudysCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
579 views40 pagesClass 9 - Cell - Structural and Functional Unit of Life
Cell- Structural and Functional unit of Life
[1] Cells are the fundamental unit of life and exist as either unicellular or multicellular organisms. [2] They were first observed under microscopes in the 17th century. [3] Cells vary in shape, size, and whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic.
Uploaded by
anyastudysCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 40