0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views1 pageDesign Process Error Avoidance Guide
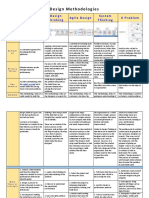
The document discusses common problems that occur when starting a design thinking project. It outlines steps to identify a shared problem, connect personal motivations to the problem, understand affected parties, and learn from past mistakes to avoid errors like focusing on solutions before fully understanding the problem.
Uploaded by
Raúl Llopis CarrascoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views1 pageDesign Process Error Avoidance Guide
The document discusses common problems that occur when starting a design thinking project. It outlines steps to identify a shared problem, connect personal motivations to the problem, understand affected parties, and learn from past mistakes to avoid errors like focusing on solutions before fully understanding the problem.
Uploaded by
Raúl Llopis CarrascoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd