0% found this document useful (0 votes)
125 views8 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Study
The document describes several experiments involving light and optics:
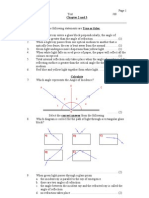
1) James shone light at a mirror and measured the angle of reflection for different angles of incidence, finding all angles were measured accurately except 60°.
2) Peter tried mixing red and green light using filters but no light reached the screen until he cut a hole in the green filter.
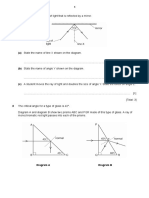
3) Another experiment involved light passing through a prism and forming a spectrum, with red at one end and blue, green, and violet in order. A green filter would cause the green part of the spectrum to disappear.
Uploaded by
dacubeguyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
125 views8 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Study
The document describes several experiments involving light and optics:
1) James shone light at a mirror and measured the angle of reflection for different angles of incidence, finding all angles were measured accurately except 60°.
2) Peter tried mixing red and green light using filters but no light reached the screen until he cut a hole in the green filter.
3) Another experiment involved light passing through a prism and forming a spectrum, with red at one end and blue, green, and violet in order. A green filter would cause the green part of the spectrum to disappear.
Uploaded by
dacubeguyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd