0% found this document useful (0 votes)
122 views16 pagesDemand Theory: Law & Elasticity Explained
h
ub
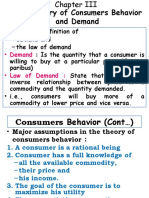
1. The document discusses the theory of demand and supply, specifically focusing on the law of demand and factors that determine demand.
2. It states that for effective demand, there must be a desire for a product, an ability to pay, and a willingness to pay.
3. Some key determinants of demand mentioned are price of the commodity, price of related/substitute goods, disposable income, population size and characteristics, and consumer preferences.
Uploaded by
wosihit898Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
122 views16 pagesDemand Theory: Law & Elasticity Explained
h
ub
1. The document discusses the theory of demand and supply, specifically focusing on the law of demand and factors that determine demand.
2. It states that for effective demand, there must be a desire for a product, an ability to pay, and a willingness to pay.
3. Some key determinants of demand mentioned are price of the commodity, price of related/substitute goods, disposable income, population size and characteristics, and consumer preferences.
Uploaded by
wosihit898Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd