0% found this document useful (0 votes)
281 views6 pagesPersonality Development
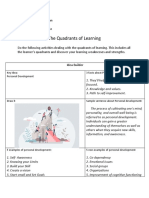
1. The document discusses five categories of personality development: mental, social, spiritual, emotional, and physical. It emphasizes the importance of developing skills in each category for personal growth.
2. Within each category, it provides examples of specific activities that can help with development, such as reading to develop mentally, improving communication skills to develop socially, and meditation to develop spiritually.
3. The document also discusses developing a positive self-image, noting that self-image is influenced by early life experiences and relationships, and shapes how we see ourselves and interact with others. It provides steps for cultivating a positive self-image, like focusing on strengths and avoiding comparisons.
Uploaded by
Joan May PolintanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
281 views6 pagesPersonality Development
1. The document discusses five categories of personality development: mental, social, spiritual, emotional, and physical. It emphasizes the importance of developing skills in each category for personal growth.
2. Within each category, it provides examples of specific activities that can help with development, such as reading to develop mentally, improving communication skills to develop socially, and meditation to develop spiritually.
3. The document also discusses developing a positive self-image, noting that self-image is influenced by early life experiences and relationships, and shapes how we see ourselves and interact with others. It provides steps for cultivating a positive self-image, like focusing on strengths and avoiding comparisons.
Uploaded by
Joan May PolintanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd