0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views21 pagesKnee Kinematics and Arthrokinematics Overview
This document summarizes knee biomechanics including:
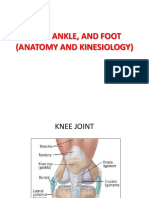
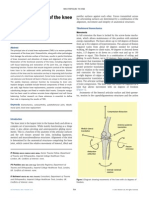
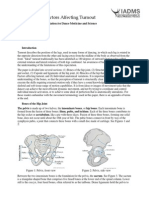
1. Flexion and extension range of motion, medial/lateral rotation, and arthrokinematics of the tibiofemoral joint.
2. How the screw home mechanism produces internal rotation of the femur during the last 20 degrees of knee extension.
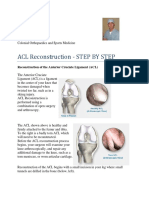
3. The role of ligaments like the ACL and PCL in controlling tibiofemoral motion during closed kinetic chain flexion and extension.
Uploaded by
birijik7979Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views21 pagesKnee Kinematics and Arthrokinematics Overview
This document summarizes knee biomechanics including:
1. Flexion and extension range of motion, medial/lateral rotation, and arthrokinematics of the tibiofemoral joint.
2. How the screw home mechanism produces internal rotation of the femur during the last 20 degrees of knee extension.
3. The role of ligaments like the ACL and PCL in controlling tibiofemoral motion during closed kinetic chain flexion and extension.
Uploaded by
birijik7979Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd