0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views8 pagesSimulation Studies On GaNInGaN Based Multi
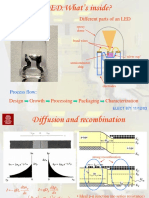
1) The document describes a simulation study on reducing efficiency droop in InGaN/GaN multi-quantum well LEDs by varying the silicon doping concentrations in the GaN barriers of the active region.
2) An improved barrier doping profile was imposed and compared to a structure with constant doping, finding improved LED performance.
3) The improved structure is attributed to decreased non-radiative recombination like Auger recombination inside the active region and reduced carrier overflow from the active region.
Uploaded by
elias srmCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views8 pagesSimulation Studies On GaNInGaN Based Multi
1) The document describes a simulation study on reducing efficiency droop in InGaN/GaN multi-quantum well LEDs by varying the silicon doping concentrations in the GaN barriers of the active region.
2) An improved barrier doping profile was imposed and compared to a structure with constant doping, finding improved LED performance.
3) The improved structure is attributed to decreased non-radiative recombination like Auger recombination inside the active region and reduced carrier overflow from the active region.
Uploaded by
elias srmCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd