0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views25 pagesJava String Class Methods Explained
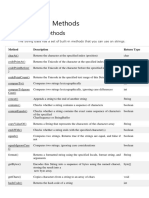
The document discusses the String class in Java, which allows the creation of objects to hold string values and provides various methods for manipulating strings, such as length(), charAt(), concat(), substring(), equals(), and contains(). It explains how string literals are stored in the string constant pool and covers examples and details of several common String class methods.
Uploaded by
shabu laloCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views25 pagesJava String Class Methods Explained
The document discusses the String class in Java, which allows the creation of objects to hold string values and provides various methods for manipulating strings, such as length(), charAt(), concat(), substring(), equals(), and contains(). It explains how string literals are stored in the string constant pool and covers examples and details of several common String class methods.
Uploaded by
shabu laloCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd