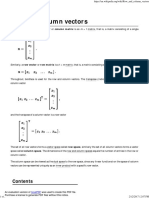
Unlocking Your Potential: Crafting the Perfect Reference Number for Your Resume
In the realm of job applications, every detail matters. Among the crucial components of a polished
resume, the reference number holds a significant place. It serves as a unique identifier for your
application, ensuring that it lands in the right hands and receives the attention it deserves. Crafting
an effective reference number can make all the difference in catching the eye of potential employers
and setting yourself apart from the competition.
At BestResumeHelp.com , we understand the importance of every element of your resume,
including the reference number. Our team of expert resume writers is dedicated to helping you
unlock your full potential and maximize your chances of landing your dream job. By utilizing our
services, you can rest assured that your reference number will be meticulously crafted to enhance the
impact of your application.
Why leave anything to chance when it comes to your career? Order now on BestResumeHelp.com
and take the first step towards securing the job of your dreams. With our professional assistance, you
can be confident that your resume will stand out for all the right reasons. Don't let a generic
reference number hold you back – trust BestResumeHelp.com to help you shine.
�The differentiation of Sinx is Cosx and here on applying the x value in degrees for Cosx we can
obtain the slope of the tangent of the curve of Sinx at a particular point. Web find the reference
angle with the help of offered degrees. Nevertheless, you can always proceed with specific steps that
will help in many forms. Start manipulating the more complicated side and transform it into more
simple trigonometric expressions. Trigonometric functions are extensively used in calculus, geometry,
algebra. As you can observe, you can cancel a lot of terms in the numerator. Generally, the area under
the graph of the trigonometric function can be calculated with reference to any of the axis lines and
within a defined limit value. Cofunction Identities in Trigonometry (With Proof and Examples)
Learn how to solve problems about cofunction identities in trigonometry. The differentiation is
calculated using the first principle of derivatives. The cotangent is the ratio of the adjacent to the
opposite. Now read your answer of sine from the triangle. Answer. This represents all the higher
angle values of Sinx. Now read your answer of cosecant from the triangle (hypotenuse over opposite
side). Answer. Remember that the reference triangle contains the reference angle. The sides of a
right triangle are the perpendicular side, hypotenuse, and base, which are used to calculate the sine,
cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant, and cotangent values using trigonometric formulas. The general
solution represents all the higher angle values of Tanx. The principal values of trigonometric
functions have been derived from a unit circle. This image is not licensed under the Creative
Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website.
Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page. The sides of the triangle can be
identified in relation to the angle as the “opposite” (the side opposite of the angle), the “adjacent”
(the side next to the angle other than the hypotenuse), and the “hypotenuse” (the side opposite the
right angle of the triangle). And the range is the highest and the lowest values which are obtained.
Here x can have values in whole numbers, decimals, fractions, or exponents. They are of particular
importance for standard position angles whose terminal sides reside in quadrants II, III and IV. This
inverse function is called the logarithmic function. This image is not licensed under the Creative
Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website.
Creating a trigonometric table can help you remember key trig formulas. Keep reading and you’ll
remember trig equations like the back of your hand! The terminal side of the angle will be a segment
of length 10 units. An angle whose measure is greater than zero but less than 90 is called an “acute
angle”. Because cosecant is the inverse of sine, it is equal to the hypotenuse divided by the opposite
side. A reference angle always uses an x-axis as its frame of reference.
�This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some
other images posted to the wikiHow website. Trigonometry Is One Of The Most Useful Topics In
Mathematics, And These Thorough, Detailed Worksheets Will Give Students A Solid Foundation In
It. 3.which of the following angles correspond to the same point on the unit circle. If the equation
involves functions of 2x and x, transform the functions of 2x into functions of x by using identities.
Example 8: Obtaining Values of Cosecant, Secant, and Cotangent Using the Triangle Illustrations
Given the following triangles, identify the values of csc (X), sec (W), and cot (R). Referring to the
triangle, the value of hypotenuse is equal to 5 while the value of the opposite side is 3. In radian
measure, the reference angle must be Identify The Principal Angle For A Given Angle, Use Principal
Angles To Find The Value Of Trigonometric Functions Where The Angles Are. Acute Angle:. o.
Initial ray. A. c. b. ?. B. C. a. Commonly used mnemonic for these ratios. We measure angles
counterclockwise from the positive. Keep reading and you’ll remember trig equations like the back
of your hand! For the three sides of the triangle as hypotenuse, base, altitude, and for the angle
between the hypotenuse and the base being ?, the value of the six trigonometric ratios is as follows.
Similarly we have the domain and range from all other functions. This image is not licensed under
the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow
website. See how their reference angles and the corresponding trigonometric ratios change in the
different quadrants. This concept can be similarly applied to all the other trigonometric functions.
Web an angle’s reference angle is the measure of the smallest, positive, acute angle t t formed by the
terminal side of the angle t t and the horizontal axis. The numbering starts from the upper right one,
the first quadrant, where both coordinates are positive as we continue to move in the anticlockwise
direction. Just like trig simplification, there is no exact recipe on how to prove trig identities. We’re
done! Proving trig identities take a lot of practice. She has an MA in Education, specializing in
Administration and Supervision from Saint Louis University. Midsegment (drag point D) Thin Slice:
Exploring Right Triangles Discover Resources Visualising Differentiation Forum 62 41843 B
TextPosition Math Untitled. The six basic trigonometric functions are sine function, cosine function,
secant function, co-secant function, tangent function, and co-tangent function. The trigonometric
functions can be used to find the height of a tree, for the given distance of the tree from the point of
observation. For an optimal experience, please switch to the latest version of Google Chrome,
Microsoft Edge, Apple Safari or Mozilla Firefox. These principal values are also referred to as
standard values of trig functions at specific angles and are frequently used in calculations. It is why
functions like secant, cosecant, and cotangent have holes or gaps in their domains. Obtaining Values
of Cosecant, Secant, and Cotangent Using the Triangle Illustrations Solution First, let us solve for
csc (X). Once you’ve created your 6 rows and columns, assign each column a number from 0-4. In
the first quadrant, the standard position angle is its own reference angle and is contained in the
reference triangle. I searched for some simple easy tricks and found this. For ?, 2? the trigonometric
values remain the same.
�Notice that there are a selected number of reference angles shown in the unit circles since they have
their in simple decimal numbers. She has an MA in Education, specializing in Administration and
Supervision from Saint Louis University. By continuing to use our site, you agree to our cookie
policy. From the given triangle, the value of hypotenuse is 10, while the value of the opposite side is
8. When our angle moves out of the first quadrant, we must be aware of the sign of our function
value. Done by: Justin Lo Lee Bing Qian Danyon Low Tan Jing Ling. Web find the reference angle
with the help of offered degrees. Memorizing trig identities will make proving trig identities 100
times easier. Also, the trigonometric functions have different values for different angle values
between the hypotenuse and the base of the right triangle. This image is not licensed under the
Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow
website. This inverse function is called the logarithmic function. Start by replacing those functions
with their equivalence. This concept can be similarly applied to all the other trigonometric functions.
It is important to not give up, if you are stumped. If the equation involves functions of 2x and x,
transform the functions of 2x into functions of x by using identities. The sides of a right triangle are
the perpendicular side, hypotenuse, and base, which are used to calculate the sine, cosine, tangent,
secant, cosecant, and cotangent values using trigonometric formulas. This image is not licensed under
the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow
website. Notice that x and y values are positive in quadrant I. Reciprocal Identities Definition Secant
The secant function is the reciprocal of the cosine. There are six trigonometric functions for any acute
angle. The reciprocal for sine function is the cosecant function. We’re here to help you remember all
kinds of trigonometric equations with easy-to-follow methods. Midsegment (drag point D) Thin
Slice: Exploring Right Triangles Discover Resources Visualising Differentiation Forum 62 41843 B
TextPosition Math Untitled. The Reference Angle Theorem states that To find the value of a
trigonometric function of any angle t. It is the hypotenuse ratio to the side adjacent to a given angle
in a right triangle. Keep reading and you’ll remember trig equations like the back of your hand!
Cofunction Identities in Trigonometry (With Proof and Examples) Learn how to solve problems
about cofunction identities in trigonometry. Often, you solve the side where you can break down
equations into uncomplicated trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent. All the
trigonometric formulas can be transformed into inverse trigonometric function formulas. These
fundamental identities are inverses of the functions.