0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes) 150 views11 pagesAnsoff Matrix
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content,
claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
ANSOFF
MATRIX (~
¥�> Objectives
- eae Uke Sem aac ~ ri
=
, [eel oul ei lel Boo)
‘
jPoce LTO
a @ Examine the Ansoff matrix for different growth
strategies of a given organization�Key Terms
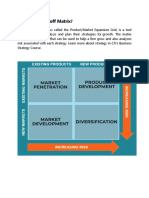
Ansoff matrix: Strategic management tool, used to devise product and market growth
strategies for an organization.
Diversification: Growth strategy in Ansoff's matrix that involves the business moving into
new markets with new products.
Market development Growth strategy in Ansoff's matrix that involves a business selling
existing products in new or unexplored markets.
Market penetration: Growth strategy in Ansoff’s matrix that focuses on developing existing
markets with existing products in order to increase sales revenue and market share.
Product development: Growth strategy in Ansoff’s matrix that involves a business
introducing new products to its existing customers.�Ansoff Matrix
PRODUCTS é
EXISTING NEW
Designed by Igor Ansoff in 1957
The matrix can be used with both e
internal and external growth
strategies.
MARKETS
Ansoff grouped the different options
for growth into FOUR categories,
based upon combinations of two
criteria: Products and Markets.
fication
Mie
NEW�Involves selling more of the same products and
services to the same customers, or at least the same
types of customers.
Usually considered the least risky growth strategy -
Focus on increase revenues
Does not allow the organization to grow and develop
as fast as it would like.
It may be that most potential customers cannot be
persuaded to buy more
Use competitive pricing, introducing customer loyalty,
widening distribution channels or more effective
promotional campaign
Market Penetration
EXISTING
PRODUCTS
EXISTING
sic
a en�Product Development
Involves selling new products within the
organization's existing market, often to e
customers.
Usually involves some risk because it requires more
investment in time and resources.
Often involves a developing modified product —
Extension strategy
Efforts may distract the owner from the core business
Efforts to sell new products may fail if managers do
not understand customers’ needs and expectations.
Depending on how loyal the customers are to the
original products
MARKETS
EXISTING
NEW�Market Development
Involves selling existing products to new customers ~
New market segments
Is considered riskier than a market penetration
strategy. This is because the organisation may not
understand the needs of the new customers, so its
offerings might not be adapted to the new market
Often involve a new geographic market, cultural clash
Can also involve selling the existing product to a new
demographic group or target market
Change the model of business B2B to B2C
MARKETS
PRODUCTS
EXISTING
Lisi
ae aaa
Nay
a�> Diversification
Involves selling new products in a new market.
=
Ss
=
Za
i
=>
=
on -
The riskiest growth strategy, as the business is
involved in activities where it may have little
knowledge.
Diversification
There is a chance of making costly mistakes.
Strategy
Unrelated diversification
NEW
MARKETS
Engaging in diversification that is unrelated to the
original business is, in most cases, the riskiest growth
strategy of all.
ec]
Titer�Summary Ansoff Matrix
Product Development
Market
Development
iversification
‘Same products for
ing customers,
New products for
existing customers
New customers for
ing products
New products for new
customers
Familiar markets
roduct extension
strategies and product
development
Familiar products
Spreading of risk
Minimal risk
Moderate risk
Moderate risk
High risk
Seek to maintain or
raise market share
Innovation to replace
existing products
Entering overseas
markets
Spreading of risk
Intense
competition
Product improvements
New distribution
channels
Use of subsidiaries and
strategic business units
Changing
marketing mix
Brand extension
strategies
Changing marketing
mix
Less focus on core markets
and competencies�Question 45.1 - Growth strategies
Use the Ansoff Matrix to explain the growth strategies in the following cases:
(a) Cadbury, the chocolate manufacturer, launches new products under the names of Créme Eggs, Flake, Crunchie and
Heroes to compete with existing rival brands. [4 marks]
{b) Toyota, the world’s largest car manufacturer, launches a new line of upmarket cars under the Lexus brand to cater for
wealthier customers. (4 marks}
(¢)_ Tesco,oneofthe world’s largest supermarket chains, expands by providing petrol and financial servicestoits customers.
[4 marks}
(d) McDonald's introduces wedding services under the McWedding brand name. [4 marks}�Question 45.2 - Adidas
According to its corporate website, Adidas strives “to be the best sports brand in the world” This mission statement is
supported by the companys growth strategy of market development across the world, in its attempt to be the global
leader in the sporting goods industry with brands built on a passion for sports and a sporting lifestyle.
The COVID-19 pandemic caused sales revenues at Adidas to fall by 16% in 2020 to €19.84bn ($22.44bn). This caused the
company to change its growth strategy to develop new distribution channels, with a shift from selling its goods in retail
outlets to using e-commerce and mail order. The company's growth strategy includes plans to double its e-commerce
business to €9bn ($10.2bn) by 2025. Source: https//wwwadidas-group.com/en/about/profie/
{a)_ Define the term market development. [2 marks}
{b) Define the term distribution channels. [2 marks}
(©) Explain one advantage and one disadvantage of Adidas’s market development strategy. [4 marks)