0% found this document useful (0 votes)
628 views23 pagesSimple Interest
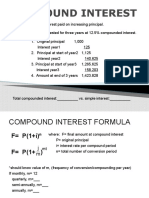
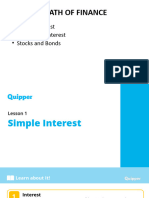
1) Simple interest is calculated by multiplying the principal, rate, and time. The formula is I = Prt.
2) The future or maturity value is calculated as F = P + I, or using the formula F = P(1 + rt).
3) Present value is the principal amount that, invested at a given rate for a period of time, will yield a future value. It is calculated as P = F/(1+rt).
Uploaded by
Arianne ValenciaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
628 views23 pagesSimple Interest
1) Simple interest is calculated by multiplying the principal, rate, and time. The formula is I = Prt.
2) The future or maturity value is calculated as F = P + I, or using the formula F = P(1 + rt).
3) Present value is the principal amount that, invested at a given rate for a period of time, will yield a future value. It is calculated as P = F/(1+rt).
Uploaded by
Arianne ValenciaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd