0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views36 pages8085 Microprocessor Instruction Set Guide
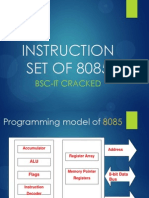
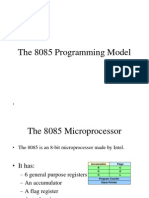
The document describes the instruction set of the 8085 microprocessor. It discusses the different types of instructions including data transfer, arithmetic, logical, branching, and control instructions. For data transfer instructions, it provides the opcode, operand, and description of various instructions like MOV, MVI, LDA, STA, XCHG, PUSH, and POP. For arithmetic instructions, it discusses addition, subtraction, increment, decrement instructions and provides examples like ADD, SUB, ADI, and SUI.
Uploaded by
ajf3215Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views36 pages8085 Microprocessor Instruction Set Guide
The document describes the instruction set of the 8085 microprocessor. It discusses the different types of instructions including data transfer, arithmetic, logical, branching, and control instructions. For data transfer instructions, it provides the opcode, operand, and description of various instructions like MOV, MVI, LDA, STA, XCHG, PUSH, and POP. For arithmetic instructions, it discusses addition, subtraction, increment, decrement instructions and provides examples like ADD, SUB, ADI, and SUI.
Uploaded by
ajf3215Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd