0% found this document useful (0 votes)
252 views2 pagesElectric Field Problems and Solutions
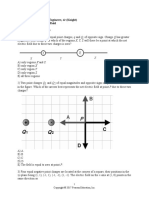
1. The document contains physics problems about electric fields and charges.
2. It includes questions about the magnitude and direction of electric fields created by point charges and charged disks, and the forces and torques exerted on particles in electric fields.
3. The problems cover topics like electric field lines, net electric field from multiple charges, field strength as a function of distance from a point charge, and the field and torque on a dipole in an external electric field.
Uploaded by
Damilola OniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
252 views2 pagesElectric Field Problems and Solutions
1. The document contains physics problems about electric fields and charges.
2. It includes questions about the magnitude and direction of electric fields created by point charges and charged disks, and the forces and torques exerted on particles in electric fields.
3. The problems cover topics like electric field lines, net electric field from multiple charges, field strength as a function of distance from a point charge, and the field and torque on a dipole in an external electric field.
Uploaded by
Damilola OniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd