0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views4 pagesMath Formula Sheet for Functions & Derivatives
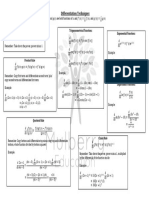
The document provides formulas and rules for topics including quadratic functions, logarithms, differentiation, integration, matrices, and revenue/cost/profit. It includes definitions, properties, and calculation rules for these mathematical and economic concepts.
Uploaded by
Yuri ParkCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views4 pagesMath Formula Sheet for Functions & Derivatives
The document provides formulas and rules for topics including quadratic functions, logarithms, differentiation, integration, matrices, and revenue/cost/profit. It includes definitions, properties, and calculation rules for these mathematical and economic concepts.
Uploaded by
Yuri ParkCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd