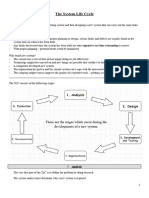
System Life Cycle
System life cycle is several stages set by the analyst to evaluate or upgrade
the current system the company works with.
Analysis
Design
Evaluation
Development
&
Documentation Testing
Implementation
(I) Analysis Stage: -
Analyze the current system: -
There are four methods to examine the current system which are:
(a) Observation.
(b) Interviews.
(c) Questionnaires.
(d) Examination of the current system.
(a) Observation: -
This method involves watching personnel using existing system to see how
it works.
1
� Advantages of observation: -
1- Analyst obtains reliable data.
2- Better getting overall viewing of the system.
3- Inexpensive method of analyzing.
4- All inputs and outputs of the system are seen.
Disadvantages of observation: -
1- People are generally feeling uncomfortable of being watched.
2- If anyone does anything against the company policy will stop when senses
he is watched.
(b) Interviews: -
A method of analyzing based on doing one to one question and
answer session between the analyst and the user.
Advantages of interview: -
1- Motivates interviewee to give honest and direct answers.
2- Analyst can go deep and extends his questions.
3- Analyst can watch body language and facial expressions.
Disadvantages of interview: -
1- Can be time consuming exercise.
2- Expensive way (Team of analysts and interviewees needed).
3- Interviewee can guess what answers analyst wants to hear.
(c) Questionnaires: -
It’s distributing questionnaires for the workforce clients and
users to find out their views and how the tasks are carried out.
Advantages of questionnaires: -
1- Questionnaires can be answered quickly.
2- Inexpensive method.
3- Individuals remain anonymous.
4- Interviewees can answer at their own time.
2
� 5- Greater number of people can be involved.
Disadvantages of questionnaires: -
1- Number of returned questionnaires always low.
2- Questions are rigid no flexibility or ability to extend it.
3- Interviewees may not take it seriously as long as they remain
anonymous.
(d) Examination of the current system: -
It allows the analyst to see:
- How files are kept.
- Operating instructions.
- Training manuals
Advantages of Examining the current system: -
1- Detailed information about the system can be obtained.
2- Analyst can see themselves how system works.
Disadvantages of examining the current system: -
1- Very large time consuming.
2- Expensive method of analyzing.
Inputs, Outputs, processing and current system problems: -
One method of analyzing data is to do Data Flow Diagram(DFD), from
it analyst can easily find out:
- Input
- Output
- Each stage problem
- The processing is being done.
- Storage may be needed.
User requirements: -
User requirements are designed to help in :
3
� - Written by the analyst for the customer (enterprise manager).
- Written in natural language and few technical terms.
- Allows customer checks what analyst exactly proposes.
Information requirements: -
This information is made up of:
- What is the system about.
- When the time this system will start to execute.
These information requirements interpreted by the analyst into
requirements specifications which are:
- Who are the customers and how they interface with the system.
- Who the vendors and how they interface with the system.
-Who are the employees and how they interface with the system.
Identification and Justification: -
This is done by analyst to identify each input, output device and
application software what their function and why we have to use it
Examples of input devices: -
Barcode (or QR code reader):-
Function: avoids manually entering of data.
Why: Error-prone and less costly on the long run.
Scanners: -
Function: Converting any printed or written paper into electronic
document.
Why: To get ride of paper-archived system which will save more space.
Touch screen: -
Function: Gathering information from business customer.
4
� Why: More effective and to ensure employees do not miss any
important data.
Examples of output devices: -
3 D printer:
Function: To does what conventional factory of producing items.
Why: Lower cost on the long run
Fewer staff employed which results in less wages paid.
Large monitors:
Function: If the customer has CAD involved activity will be interactive
to show the employees how things are done.
Why: Less expensive than having laptop or PC for each one.
Operating system and application system: -
Operating system: Seeing which operating system fits perfectly for the
customer needs.
Function: To serve the customer requirements and run the system
smoothly
Why: making an interface or mean of communication between the
manger and the employees.
Application system: Those divided into two main categories which are
(a) Off-the-shelf: Which is ready made application software all the
manager or customer has to just buy it or get it from the stock.
Function:- Doing specific tasks such as calculations, designing.
Why: Saving the development cost which could be huge.
(b) Bespoke Software (Custom-made): Which means a software
designed or tailor-made according to the customer prerequisites.
5
� Function: Doing what asked for in an efficient and quick manner.
Why: Since what customer or manager requests is not available in the
off-the-shelf software or will not satisfy all what he/she needs.
(II) Design Stage: -
A stage follows the analysis stage which takes place in four steps:
1- File structure and data structure.
2- Input formats and data capture formats.
3- Output formats, screen layouts and report formats.
4- Validation routines.
1- File structures and data structures: -
Any document in the electronic format saved in the format of file.
A file is made up of many records.
Each record is made up of fields.
Each field holds a single type of data.
- Out of all those fields there is only one stand as Primary Key which
is uniquely identifies the record.
Field 1 Field 2 Field 3 Filed 4 Field 5
Product_ Manufacture Product_description Price $ Department
code _Year
Record 1 T4131618 2022 Digital camera $405.00 T
Record 2 T5552200 2021 Memory card $35.50 T
Record 3 A3110011 2020 Tripod for T4131618 $220.00 A
Record 4 A567777 2021 Case for T4131618 $55.57 A
Record 5 B1110000 2022 Extra battery $85.50 B
- From the table above the requirements for each field are:
• Being identified uniquely from the rest as in Product Code.
6
� • Having a specified length which will be helped in the
storage process.
• Classified under certain data type.
Data type: -
What each field being classified under.
Data types of fields are:
(a) Alphanumeric: It stores data characters letter or text along
with numeric(number) data. E.g., A134F25, C001T78G.
(b) Character: Stores only single letter or text e.g., D or X
(c) Text: String of letters or numbers or other symbols.
(d) Boolean: Logical decision based on answering or stating fact
e.g., (Yes/No or True/False).
(e) Numeric: This one used to store the numeric data used in
performing calculations.
These numeric data have several types which are:
(I) Integer (Whole number): the number doesn’t have decimal
part (e.g., 534, 10089).
(II) Decimal (Real): A number that having decimal part in it (e.g.,
3.4, 500.6)
(III) Currency: A numeric data added to it the currency symbol
(e.g., $34.5, £100, €90.56).
(IV) Date/time: This type of numeric data allows date and time
to be stored (e.g., 05/3/2023, 1:30).
From the table above we can classify the fields as follows:
7
� Field name Field length Data type
Product_code 30 Text
Manufacture_ year 4 Numeric: integer
Product_description 40 Text
Price $ 6 Numeric: Currency
Department 1 Character/ Text
Validation routine: -
Validation is the process of checking the data entered into computer
are meeting certain criteria.
Validation check is having six types which are:
(a) Range: -
Is validation check to insure if the data input lies between upper
and lower values (e.g.,
(b)Type/Character: -
Is validation check makes sure the type of data entered is correct (
letters or numbers only) e.g., ( name of person or weight of person).
(c) Length: -
Is validation check ensuring the data entered match the exact number
of characters no more no less (e.g., the telephone number shouldn’t be less
or more than 8 numbers).
(d) Format: -
Is validation check ensures that the data entered is having the correct
format (e.g., the currency format must have numbers associated with the
money sign $, €, £, ¥).
8
� (e) Presence: -
Is validation check ensures the required data is existed (e.g., in the
registration form the password field shouldn’t be skipped or left empty).
(f) Check digit: -
Is validation check ensuring there is extra digit added to the number
which calculated from the other digits.
e.g.,
• If two digits transposed during input for example 675 instead of 765.
• An incorrect digit is entered 7665 instead of 765.
• A digit is missed or extra digit added for example 7657 or 76 instead of
765.