0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views32 pagesSpecial-Purpose Diodes Overview
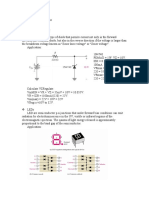
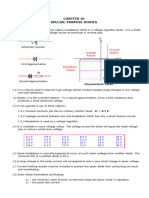
The document discusses several types of specialized diodes including Zener diodes, varactor diodes, light emitting diodes, photodiodes, laser diodes, Schottky diodes, PIN diodes, tunnel diodes, and step recovery diodes. It provides details on the characteristics and operation of each diode type.
Uploaded by
s231060031-5Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views32 pagesSpecial-Purpose Diodes Overview
The document discusses several types of specialized diodes including Zener diodes, varactor diodes, light emitting diodes, photodiodes, laser diodes, Schottky diodes, PIN diodes, tunnel diodes, and step recovery diodes. It provides details on the characteristics and operation of each diode type.
Uploaded by
s231060031-5Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd