0% found this document useful (0 votes)
113 views1 pageNull Modem vs. Straight-Through Cables
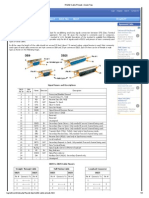
The document discusses two types of serial cables - straight through and null modem. A straight through cable connects a DTE device like a PC to a DCE device like a modem, without crossing lines. A null modem or crossover cable connects two DTE devices and crosses the transmit and receive lines between the devices.
Uploaded by
jolteon619Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
113 views1 pageNull Modem vs. Straight-Through Cables
The document discusses two types of serial cables - straight through and null modem. A straight through cable connects a DTE device like a PC to a DCE device like a modem, without crossing lines. A null modem or crossover cable connects two DTE devices and crosses the transmit and receive lines between the devices.
Uploaded by
jolteon619Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd