0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views29 pagesStrategic Marketing Planning Process
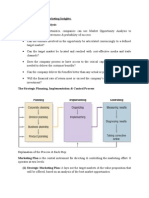
The document discusses the process of strategic marketing planning, including defining the business, analyzing the internal and external market environments, and using tools like SWOT analysis and BCG matrix analysis. Strategic planning involves systematically outlining an organization's vision, mission, scope, and environmental analysis to guide its marketing activities.
Uploaded by
nur lynndaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views29 pagesStrategic Marketing Planning Process
The document discusses the process of strategic marketing planning, including defining the business, analyzing the internal and external market environments, and using tools like SWOT analysis and BCG matrix analysis. Strategic planning involves systematically outlining an organization's vision, mission, scope, and environmental analysis to guide its marketing activities.
Uploaded by
nur lynndaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd