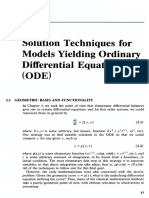
CHAPTER THREE
GENERAL SOLUTIONS TO LINEAR EQUATION
3.1 LINEAR EQUATIONS OF ORDER ONE
1.Definition
If a certain equation is not exact, it is essential to seek an
alternate way to make that equation to be exact. One way is by
means of introducing an appropriate factor called integrating
factor. The standard form for the linear equation of order one is;
dy
+ P(x)y = Q(x).
dx
Things to Remember:
“In integrating the exact equation that the integral of the left
member is always the product of the dependent variable and the
integrating factor used.”
2. Derivation of General Solution of the equation:
By definition, the equation that is linear and of order one in the
dy
dependent variable y is in the form of A(x) + B(x)y = C (x), by
dx
dividing each term of this equation by A(x) we obtain,
LSG1
�LSG2
�Thus, from the general solution equation, and by substituting the
given values;
LSG3
�LSG4
�LSG5
�Therefore;
LSG6
�LSG7
� Exercise Problem 3.1:
3.2 INTEGRATING FACTORS FOUND BY INSPECTION
Integrating factors found by inspection is one of the additional topics
on Equations of Order One. In the previous lesson to be more specific
we found that any linear equation of order one can be solved with the
help of an integrating factor. In this lesson we are concerned with
equations that are enable us to determine integrating factors found by
inspection.
1.Definition
Recognition of common exact differentials that occur frequently is
very important in order to develop the ability in dealing and solving
of this type of problems.
LSG8
�Things to Remember:
A differential involving only one variable like 2 dx x is an exact
differential.
EXAMPLE PROBLEM I:
Solve the equation ydx + (x + x3y)dy = 0
Solution:
The given equation is ydx + (x + x 3y)dy = 0
Evaluate the given equation and group the terms of like degree,
LSG9
�EXAMPLE PROBLEM 2:
LSG10
� EXERCICES 3.3:
3.3 DETERMINATION OF INTEGRATING FACTORS
Definition
In dealing of the differential equation Mdx Ndy + = 0, the
following conditions must be satisfied
LSG11
�LSG12
�LSG13
�LSG14
� EXERCISE 3.3:
3.4 SUBSTITUTION SUGGESTED BY THE EQUATION
The equation in the form of Mdx + Ndy = 0 may not bring in at
once or at all to the previous methods involving this kind of equation.
We can deal also to this equation by means of changing some of its
variables to transform the equation into a type that we know how to
solve.
LSG15
�LSG16
�EXAMPLE PROBLEM 2:
LSG17
�LSG18
�3.5 BERNOULLI’S EQUATION
LSG19
�EXAMPLE PROBLEM I:
LSG20
�LSG21
�LSG22
�EXAMPLE PROBLEM 2:
LSG23
�EXAMPLE PROBLEM 3:
LSG24
�LSG25
�EXERCISES 3.5:
LSG26
�3.6 COEFFICIENTS LINEAR IN THE TWO VARIABLES
EXAMPLE PROBLEM I:
LSG27
�LSG28
�EXAMPLE PROBLEM 2:
LSG29
�LSG30
�EXERCISES 3.6
LSG31