Home / Home Loan / Repo Rate 2024
Current Repo Rate 2024
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) announced
on 8 June 2023 that the repo rate was increased by
25 basis points.This makes the current repo rate
6.50% (from the 6.25% that it was earlier).
The reverse repo rate stands unchanged at
3.35%.The Bank Rate and the Marginal Standing
Facility (MSF) rate has changed to 6.75%.The
Standing Deposit Facility Rate is 6.25%.
What is REPO Rate?
Repo rate is defined as the rate of interest at which the
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) lends money to commercial
banks.
''Repo'' stands for Repurchase Agreement or
Repurchasing Option. Banks avail loans from the central
bank (the RBI) by selling eligible securities.
An agreement between the central bank and the
commercial bank will be made to repurchase the
securities at a price that is predetermined. This is done
when banks face a shortage of funds or need to maintain
liquidity in volatile market conditions.
The RBI uses the repo rate to control inflation rates.
RBI Repo Rate
Repo Rate 6.50%
Bank Rate 5.15%
Reverse Repo Rate 3.35%
Marginal Standing Facility Rate 6.75%
Find REPO Linked: Home Loan Interest Rate
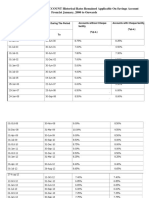
RBI Repo Rate Cut History 2023 -2005
The change in repo rate in India since October 2005 can
be summed up as follows:
Effective Date Repo Rate %Change
8 June 2023 6.50% 0.25%
8 February 2023 6.50% 0.25%
7 December 2022 6.25% 0.35%
30 September 2022 5.90% 0.5%
5 August 2022 5.40% 0.5%
8 June 2022 4.90% 0.5%
May 2022 4.40% 0.4%
09 Oct 2020 4.00% 0.00%
06 Aug 2020 4.00% 0.00%
22 May 2020 4.00% 0.40%
27 March 2020 4.40% 0.75%
6 February 2020 5.15% 0.25%
07 August, 2019 5.40% 0.35%
06 June, 2019 5.75% 0.25%
04 April, 2019 6.00% 0.25%
07 February, 2019 6.25% 0.25%
01 August, 2018 6.50% 0.25%
06 June, 2018 6.25% 0.25%
02 August, 2017 6.00% 0.25%
04 October, 2016 6.25% 0.25%
05 April, 2016 6.50% 0.25%
29 September, 2015 6.75% 0.50%
02 June, 2015 7.25% 0.25%
04 March, 2015 7.50% 0.25%
15 January, 2015 7.75% 0.25%
28 January, 2014 8.00% -0.25%
29 October, 2013 7.75% -0.25%
20 September, 2013 7.50% -0.25%
03 May, 2013 7.25% -0.50%
17 March, 2011 6.75% -0.25%
25 January, 2011 6.50% -0.25%
02 November, 2010 6.25% -0.25%
16 September, 2010 6.00% -0.25%
27 July, 2010 5.75% -0.25%
02 July, 2010 5.50% -0.25%
20 April, 2010 5.25% -0.25%
19 March, 2010 5.00% -0.25%
21 April, 2009 4.75% 0.25%
05 March, 2009 5.00% 0.50%
05 January, 2009 5.50% 1.00%
08 December, 2008 6.50% 1.00%
03 November, 2008 7.50% 0.50%
20 October, 2008 8.00% 1.00%
30 July, 2008 9.00% -0.50%
25 June, 2008 8.50% -0.50%
12 June, 2008 8.00% -0.25%
30 March, 2007 7.75% -0.25%
31 January, 2007 7.50% -0.25%
30 October, 2006 7.25% -0.25%
25 July, 2006 7.00% -0.50%
24 January, 2006 6.50% -0.25%
26 October, 2005 6.25% 00.00
How Does Repo Rate Work?
As mentioned earlier, the repo rate is used by the central
bank of India to control the flow of money in the market.
When the market is hit by inflation, RBI increases the
repo rate. An increased repo rate denotes that the banks
who borrow money during this period from the central
bank will have to pay higher interest. This discourages
the banks to borrow money, which in turn, reduces the
supply of money in the market and helps negate the
inflation. Similarly, the repo rates are decreased in the
case of a recession.
How Does RBI Calculate Repo Rate?
On the basis of the economic condition, as discussed in
the last paragraph, the RBI regulates the repo rate. The
rates are decided by the central bank on the basis of the
inflation or recession in the market of the country.
Calculate your Home Loan EMI
Repo Rate vs Reverse Repo Rate
Repo Rate vs Reverse Repo Rate is one of the most
important topics that we need to understand. The
difference can be listed as follows:
1. Repo rate is charged against funds lent by the RBI
to commercial banks and other financial
institutions.The reverse repo rate, on the other
hand, is the rate of interest that is offered by the
central bank to the commercial banks who deposit
funds in the RBI treasury.
2. Repo rate is always higher than the reverse repo
rate.
3. Repo rate helps to control the inflation in the
market. The reverse repo rate, on the other hand,
helps to control the supply of money in the market.
What is the Difference between the Repo
rate and the MCLR rate?
Marginal Cost of funds based Lending Rate or MCLR is a
reference rate which is used internally for ascertaining
the interest rate which can be levied by the banks on
loans.
The repo rate, on the other hand, is an interest rate
which is determined by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
and charged against the funds lent by the central bank to
commercial banks and all other financial institutions.
What effect does Repo Rate has on the life
of a common man?
The effect of repo rate on the life of common man is
direct in terms of the increase in the overall interest. As
discussed earlier, repo rate is the rate of interest which
is charged by the RBI for funds lent to the commercial
banks.
When the repo rate increases, the interest rate at which
commercial banks borrow money from the central bank
increases and the borrowing becomes costlier. In turn,
the commercial banks increase their lending rates to
cope up with the hike in the repo rate. Thus, when
common men borrow money from the commercial
banks, the effective interest rate becomes higher and
they end up paying higher interest amounts for the loan
that they borrow.
What is the relationship between Inflation
and Repo Rate?
The repo rate is used by the central bank of India to
control the supply of money in the Indian market. A
higher repo rate helps in reducing the borrowing power
of the commercial banks which, in turn, reduces the flow
of cash in the market. This method helps to control
inflation.
Let us take an example here. Let us assume that the
country has been hit by inflation and the RBI has set the
repo rate at 10%. In this case, if a commercial bank is
borrowing an amount of Rs.10,000 from the central
bank, the interest amount for the same will be Rs.1,000.
To avoid paying this higher rate of interest, the
commercial banks decide to not borrow further from the
RBI which reduces the supply of cash in the market. As
the flow of cash reduces in the market, the demand is not
met. This helps in checking the inflation and regulating it
accordingly.
FAQs on Current Repo Rate 2023
1. What is repo rate?
Repurchase Agreement or Repurchasing Option is
referred to as "repo." The Reserve Bank of India
(RBI) uses the repo rate as an interest rate,when
lending money to commercial banks to control
inflation rates.
2. What is reverse repo rate?
The interest rate that the central bank offers to
commercial banks that deposit money in the RBI
treasury is known as the reverse repo rate.
3. What is the difference between repo rate
and reverse repo rate?
The RBI charges a repo rate on the money it lends
to commercial banks and other financial institutions
while the interest rate that the central bank offers
to commercial banks that deposit money in the RBI
is the reverse repo rate.Reverse repo rate is never
greater than repo rate.Repo rates assist in reducing
market inflation.On the other hand,the reverse
repo rate aids in regulating the amount of money
available in the market.
4. What is the Marginal Cost of Funds Based
Lending Rate?
The Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate,
also known as MCLR,is a benchmark rate that
banks use internally to determine the maximum
interest rate they can charge borrowers.
5. What types of loans are impacted by the
reduction or increase in repo rates?
A reduction or increase in the repo rate will affect
loans like personal,vehicle,home,and gold loans.
6. How frequently will banks alter loan interest
rates that are tied to the repo rate?
Guidelines established by the Reserve Bank of India
state that interest rates based on an external
benchmark interest rate must be revised every 3
months.
News about Repo Rate Hike
RBI's Decision to Maintain Repo Rate at 6.5%
to Provide Relief for Individuals with Home
Loan
The significant relief that home loan borrowers received
was a much-needed halt to the relentless escalation of home
loan interest rates, as the RBI chose to maintain the repo
rate during its April MPC meeting this year. The RBI's
decision to uphold the repo rate at 6.5% since February of
this year will continue to provide relief for homebuyers
dependent on EMIs.
This recent status quo marks the third consecutive pause in
repo rates following a series of increases that commenced in
May 2022 and extended until February. The primary
mandate of the RBI has been to maintain retail inflation
within the range of 2-6%. In May 2022, the same month
when the RBI initiated the first repo rate increase of the
current cycle, retail inflation peaked at 7.79%. The assertive
repo rate hikes enabled the RBI to bring inflation below 5%
for the first time in April 2023, leading to its decision to
pause the interest rate hikes.
12 August 2023
Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) keeps the
repo rate unchanged
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI)'s MPC in its second monthly
monetary policy meeting of Financial Year 24 has decide to
keep the repo rate unchanged 6.50%. The RBI effectively
delivered a hawkish pause, holding the policy rate at 6.5%
but leaving the door open for future rate action.
8 June 2023
RBI is expected to keep its key interest rates
unchanged at 6.50%
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is expected to keep the key
interest rates unchanged at 6.50% despite the fall in the
inflation rate to 4.70% in April 2023. The repo rate is
recorded to remain unchanged and is also expected to
remain at a rate less than 6.75% terminal rate for the rest of
the year.
31 May 2023
RBI Hikes Repo Rate to 6.5%
The Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) Monetary Policy
Committee (MPC) announced an increase in the repo rate
by 25 basis points to 6.5% on 8 February, as revealed by
Governor Shaktikanta Das. The Governor stated that the
global economy has improved and inflation is decreasing. He
added that the MPC decided with a 4:2 vote to continue
with the withdrawal of the accommodative policy. The real
GDP growth for 2023-24 is estimated at 6.4%, and the
Indian economy remains resilient, despite global
uncertainty, Das stated. Retail inflation is predicted to reach
an average of 5.6% in the fourth quarter, and the CPI
inflation for 2022-23 is projected at 6.5%, according to Das.
To curb inflation, primarily caused by external factors such
as the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the Reserve Bank of India has
increased the short-term lending rate by 250 basis points
since May of last year.
8 February 2023
Home Loans by Banks
Home Loans by NBFC
Home Loan Articles
Home Loan Resources
• Home Loan Interest Rate
• Repo Rates
• MCLR Rates
• Home Loan Processing Fee
• Home Loan Documents Required
• Compare Plot Loan
• Home Loan Tax Benefits
Schemes and Acts
• Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana
• PMAY Gramin
• PMAY Urban
• RERA Act
• Stamp Duty Charges
• Encumbrance Certificate
• DDA Housing Scheme
Calculator
• Home Loan EMI Calculator
• Home Loan Eligibility Calculator
• Home Loan Balance Transfer Calculator
• Home Loan Prepayment Calculator
• Home Loan Repayment Calculator
• Land Conversion Calculator
• Home Loan Affordability Calculator
Disclaimer
Explore More
Credit Card
Credit Score
Personal Loan
Home Loan
Fixed Deposit
Calculator
Others
Learn More
Mobile Apps
About Careers Contact Us Blog Terms
Notice to customer
Copyright © 2024 BankBazaar.com. Privacy Policy