0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views6 pagesImpact of Wolves on Yellowstone Ecosystem
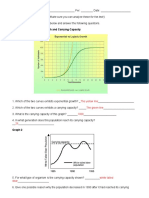
The document discusses the dynamics of wolf and moose populations in Yellowstone, defining key ecological terms and explaining the impact of wolf elimination on the ecosystem. It highlights the significance of Yellowstone as the first national park and the economic benefits it brings, alongside the ecological consequences of predator removal. Additionally, it addresses the use of double-y axis graphs for visualizing predator-prey relationships and the purpose of environmental impact statements.
Uploaded by
m6wjgjm2y7Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views6 pagesImpact of Wolves on Yellowstone Ecosystem
The document discusses the dynamics of wolf and moose populations in Yellowstone, defining key ecological terms and explaining the impact of wolf elimination on the ecosystem. It highlights the significance of Yellowstone as the first national park and the economic benefits it brings, alongside the ecological consequences of predator removal. Additionally, it addresses the use of double-y axis graphs for visualizing predator-prey relationships and the purpose of environmental impact statements.
Uploaded by
m6wjgjm2y7Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd