0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views8 pagesHerons Formula Qa
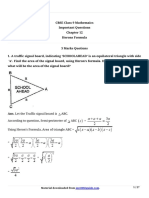
The document is a test paper on Heron's Formula, containing various questions related to calculating areas of different geometric shapes, including triangles, parallelograms, and trapeziums. It includes problems involving equilateral and isosceles triangles, as well as quadrilaterals, with some questions requiring the application of formulas to find missing dimensions. Solutions are provided for each question, illustrating the methods used to arrive at the answers.
Uploaded by
Kaustubh MohapatraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views8 pagesHerons Formula Qa
The document is a test paper on Heron's Formula, containing various questions related to calculating areas of different geometric shapes, including triangles, parallelograms, and trapeziums. It includes problems involving equilateral and isosceles triangles, as well as quadrilaterals, with some questions requiring the application of formulas to find missing dimensions. Solutions are provided for each question, illustrating the methods used to arrive at the answers.
Uploaded by
Kaustubh MohapatraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd